Drawing Shapes.
Use Polymorphism and Abstraction to draw shapes.
Check you understanding.
The first list if for the students how want to deepen or (check) their understanding of the basic mechanism of polymorphism.
Polymorphism Mystery 1
The exercise is from CodeStepByStep and fill the missing boxes.
Polymorphism Mystery 2
Same question for the second example CodeStepByStep.
Abstract Shape drawing
In this lab, we will use polymorphism and Abstraction to display shapes in
Canvas defined as GWindow. The GWindow provides graphical window that supports simple graphics. It includes several methods to draw lines, rectangles and ovals.
In order to draw all those objects using the same class (called Artist),
we will use polymorphism and abstraction to represents all these forms as an abstract class called Shape.
The starting code for this project is in shapes.zip .
Here is the UML class diagram for this project:
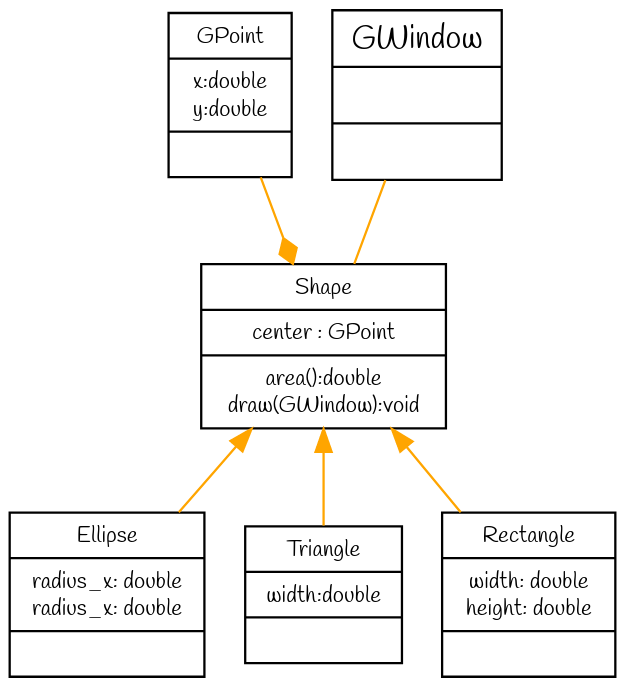
Some remarks on this diagram:
-
The relation between
ShapeandGPointis called an Composition that indicates that an object of the class Shape has-a GPoint as it center. - The second intersting relation is the once that rely
ShapeandGWindow. This relation exists since one of theShapemethods (draw) uses a Gwindow as a parameter. - The third relation between the conrete class and the
Shapeis an Inheritance class.
the GPoint class is used to represent a positioin in the 2D plan. The class two constructors and a toString() method to convert into a string.
class GPoint{
public:
GPoint();
GPoint(double x, double y);
string toString()const;
private:
double x;
double y;
};
Class Shape
The class Shape is an Abstract class to regroup all the common features
between the shapes. For the case of simplicity, we will only keep the following
aspects:
GPoint: the center of any shape.area: method to compute the area of the shape (pure function).draw(GWindow): abstract method to draw the shape in a GWindow.
Here is the content of this class:
// Define the abstract class Shape
// to represent all the shapes
class Shape
{
public:
//default constructor
// create a shape in (0,0)
Shape() : pos(0,0){}
//Create a shape in (x, y)
Shape(double x, double y): pos(x, y){}
// Area of the shape (abstract)
virtual double area() const = 0;
//Drawing in a window
virtual void draw(GWindow & canvas) const = 0;
// modifiers
void set_position(double x_pos, double y_pos)
{
pos.x = x_pos;
pos.y = y_pos;
}
// Accessser
double get_x_pos() const {return pos.x;}
double get_y_pos() const {return pos.y;}
private:
// position of the shape
GPoint pos;
};
As you could read the two following methods are pure. Meaning that they mus tbe implemented in the Inherited classes.
double area()const = 0void draw(GWindow &) const = 0;
The Ellipse class
Your first task is to implement the class ellipse that inherite from the
Shape class. In addition to its center, the ellipse will be represented by
its
x_radiusy_radius
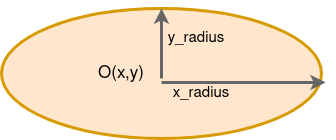
- Check the method
drawOvalin theGWindowclass.
Be careful about the arguments, especially the center and the radius.
The Rectangle class.
Similar to the Ellipse, a Rectangle is a class that inherits from the
Shape class and used to represented a rectangle with a given width and
height.
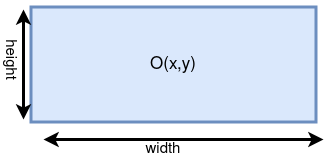
Look for a method called
drawRectin GWindow but be careful about the arguments.
Triangle class.
The final class, you should implement is the Triangle class. In order to
simply to drawing mecanism, we will only consider equilateral triangles.
Hence a trianle will be represented by it center and width as shown in
the figure:
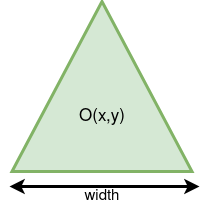
In order to draw this shape, you should look for
drawPolygonwhichs receives a list ofGPoint.
Final form
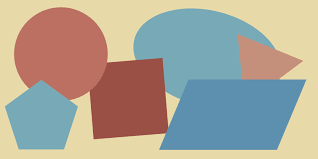
Once you completed those classe correctly, make sure the programe outputs the following form:
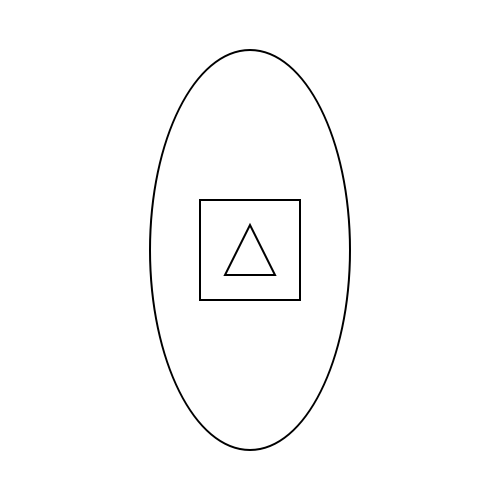
Coloreful shapes
Now suppose your boss suddently chaned his mind, and he wants a colorful shapes as shown in the figure:
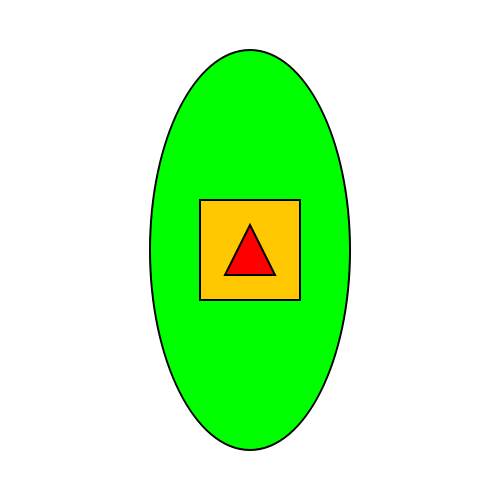
Think of a minimal change to your code in order to add this feature.
This change will push you to appreciate the abstraction aspect of programming.
ChessBoard
If your feeling adventurious, change the main.cpp file in order to print
chessboard.

- You’ll have to draw and fill all the rectangles.
- You’ll also need to add a new
Shapein order to represents the pieces.
Good luck.